Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are revolutionizing modern warehouses and manufacturing facilities, enabling high efficiency, safety, and scalability in material handling. Traditional forklifts often require skilled operators and are prone to human error, whereas AGVs provide autonomous navigation, precise control, and continuous operation.
In the era of e-commerce and rapid logistics, companies increasingly rely on forklift AGVs to meet the rising demand for faster fulfillment, better space utilization, and cost reduction. This guide covers the core functions, control system architecture, navigation technologies, and future trends of forklift AGVs, giving warehouse managers, logistics engineers, and operational planners a clear understanding of how to implement intelligent material handling solutions.
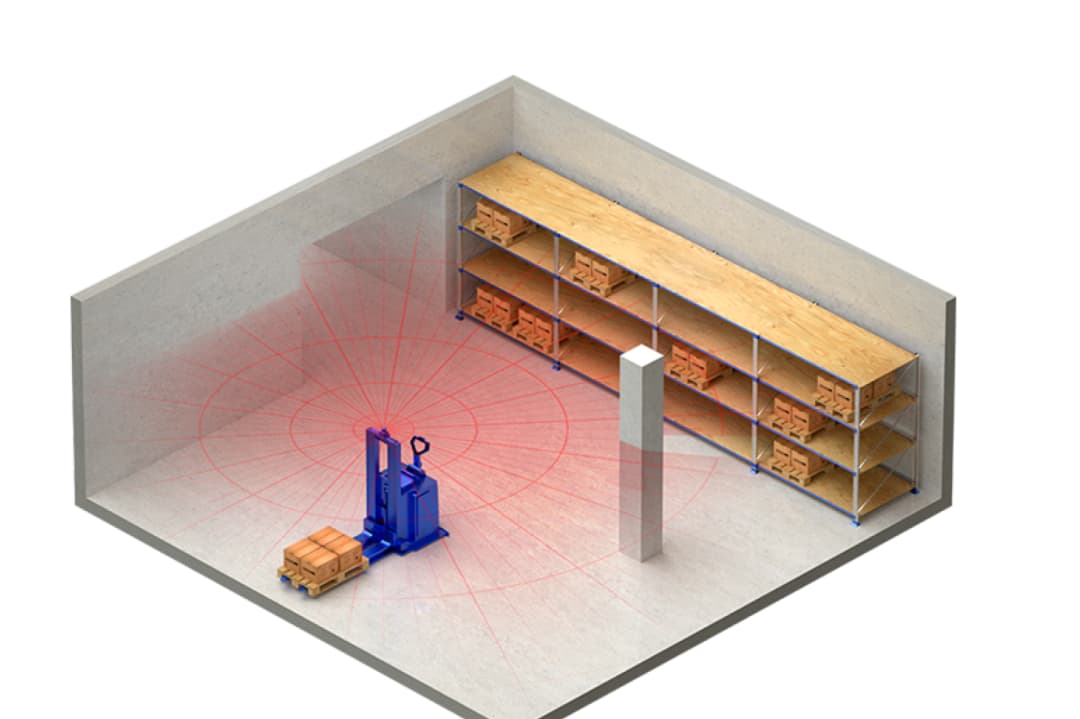
1. Core Functions of Forklift AGVs
1.1 Basic Modules of a Forklift AGV
A single-steer forklift AGV consists of several key modules:
| Module | 기능 |
|---|---|
| Laser Scanner | Provides navigation and positioning via reflectors or environmental contours |
| Touchscreen | Displays vehicle status, including battery level, operation mode, and alerts |
| Emergency Stop Button | Ensures safety by immediately stopping the vehicle in emergencies |
| Vehicle Controller | Core system controlling motion, steering, and posture |
| Safety Sensors | Detect obstacles for automatic speed reduction or stopping |
| Safety Bumpers | Prevent collisions with walls, shelves, and personnel |
| Load Switch | Detects whether the forklift is carrying cargo for automated operation |
These modules allow the forklift AGV to operate autonomously, perform repetitive tasks with high accuracy, and improve operational efficiency and safety in both small and large-scale warehouses.
1.2 Operational Benefits
-
Continuous Operation: AGVs can work 24/7 with minimal human intervention.
-
Reduced Labor Costs: Fewer operators are needed, freeing staff for higher-value tasks.
-
Enhanced Safety: Built-in sensors and safety mechanisms reduce workplace accidents.
-
Consistency & Accuracy: Automated navigation ensures precise material handling and minimizes product damage.
2. Forklift AGV Control System Architecture
그리고 Vehicle Controller is the core of any AGV system, responsible for managing the motors, sensors, and communication modules. It connects to all devices via CANOPEN or similar industrial communication protocols, ensuring real-time control.
2.1 Single-Steer Forklift Architecture
For single-steer forklifts:
-
Steering AC Motor & Drive (Steer ACD): Controls steering angle and provides feedback via encoders.
-
Driving AC Motor & Drive (Drive ACS): Manages forward/backward motion with closed-loop feedback.
-
I/O Module (Vehicle I/O Controller VMC20): Extends system capabilities for lighting, buttons, and safety features.
-
Handheld Controller (MCD8): Enables manual driving during setup, testing, or exceptional cases.
This architecture supports multiple configurations and is ideal for medium-duty warehouses with standard aisle widths.
2.2 Dual-Steer Forklift Architecture
Dual-steer forklifts have two sets of steering/driving motors: front and rear. This setup allows:
-
Advanced maneuverability: including sideways movement and precise turning in tight spaces.
-
Adaptability for heavy loads: Suitable for high-density storage or narrow aisle operations.
-
Complex control systems: requiring additional CANOPEN devices for multiple axes and sensor feedback.
Dual-steer forklifts are often deployed in industrial and manufacturing environments, where flexibility and precision are critical.
3. Navigation Technologies for Forklift AGVs
Accurate navigation is essential for AGVs to operate autonomously. Current navigation technologies include laser navigation, magnetic navigation, inductive wire navigation, and QR code navigation.
3.1 Laser Navigation
Laser scanners detect reflectors or warehouse contours for positioning:
-
Reflector-Based Navigation: Uses reflectors installed at fixed locations. With modern reflector navigation 2.0, only two reflectors are needed, reducing installation effort.
-
Natural Navigation: Uses the natural contours of the environment. No reflectors are needed, but dynamic changes in warehouse layouts can affect accuracy.
Laser navigation is highly suitable for large warehouses and manufacturing floors where consistent accuracy is required.
3.2 Magnetic Navigation
-
Magnetic Peg Navigation: Sensors detect magnetic pegs embedded in the floor. Suitable for environments where reflectors cannot be used.
-
Magnetic Tape Navigation: Continuous magnetic paths guide the AGV. Square magnetic blocks on the tape provide longitudinal updates. Ideal for confined spaces and outdoor areas.
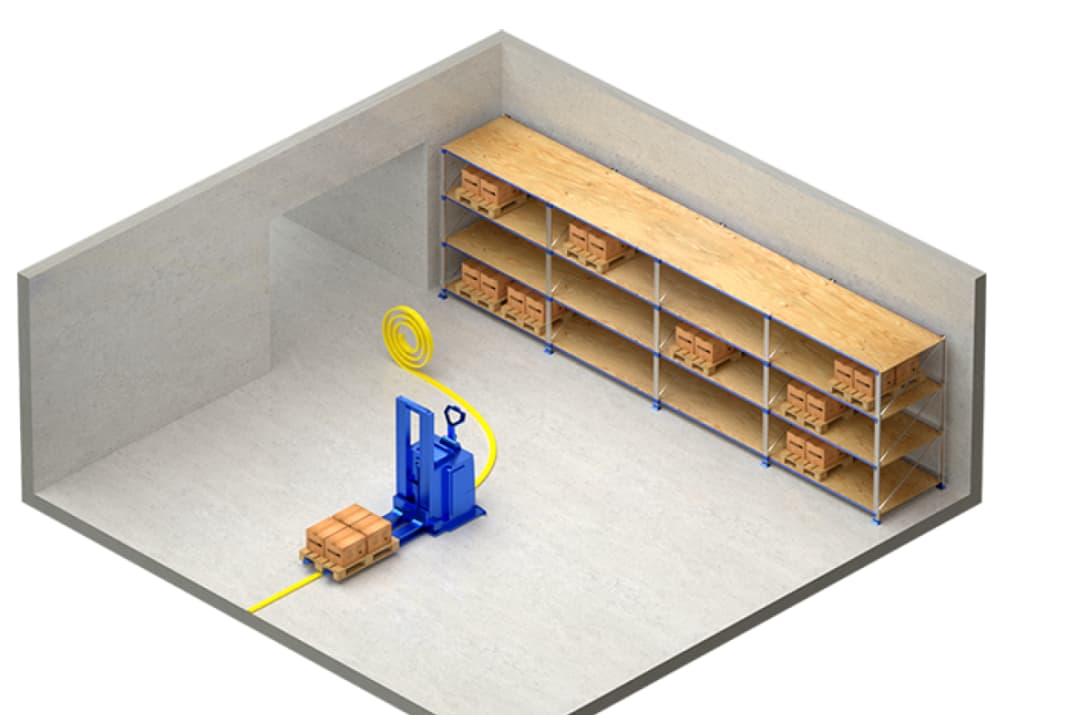
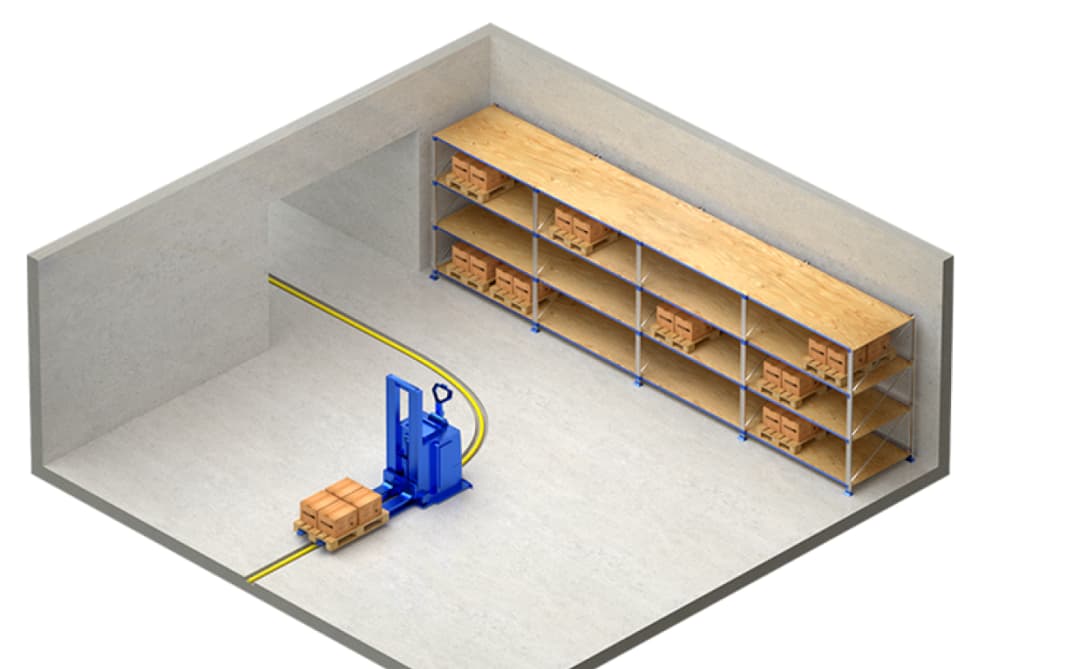
3.3 Inductive Wire Navigation
Inductive wire navigation uses underground energized wires detected by electromagnetic sensors. Though traditional and equipment-intensive, it provides continuous positioning in marker-free environments.
3.4 QR Code Navigation
QR code navigation reads floor-mounted QR codes using scanners. This method is increasingly popular in e-commerce and hospital logistics, offering:
-
High flexibility: QR codes can be relocated easily.
-
Dynamic adaptability: Path redesign is simple as storage layouts change.
-
Combined accuracy: Works with IMU and encoder feedback for precision.
4. Future Trends in AGV Navigation
4.1 Reducing Artificial Markers
The trend is moving towards markerless navigation using laser scanners or vision systems. Reducing reflectors and other markers simplifies installation and lowers maintenance. Advanced technologies like Hybrid Navigation 2.0 integrate multiple navigation methods, dynamically selecting the most accurate system for each warehouse zone.
4.2 Hybrid Navigation Systems
Hybrid navigation enables seamless switching between navigation types:
-
Wide Aisles: Use reflector or natural navigation.
-
Narrow Aisles or High-Density Storage: Switch to magnetic or QR code navigation.
This approach optimizes operational efficiency, reduces reliance on artificial markers, and improves adaptability in complex warehouse layouts.
5. Advantages of Akuros Forklift AGVs
-
Scalable Solutions: From small warehouses to large industrial facilities.
-
High Flexibility: Supports multiple navigation types and vehicle configurations.
-
Safety First: Built-in sensors, bumpers, and emergency systems protect personnel and cargo.
-
Energy Efficient: Optimized motor control reduces power consumption.
-
Future-Ready: Compatible with warehouse management systems and IoT integration.
6. Practical Applications
-
E-commerce Fulfillment Centers: Quick picking and replenishment.
-
Manufacturing Plants: Automated transport of raw materials and finished goods.
-
Cold Storage: High-precision navigation for sensitive inventory.
-
Hospital & Medical Logistics: Safe, clean, and reliable autonomous transport.
By deploying AGVs, organizations reduce labor dependency, increase throughput, and achieve better utilization of warehouse space.
결론
Forklift AGVs are an essential part of modern warehouse automation, offering precision, safety, and scalability. With advanced control systems, versatile navigation technologies, and modular designs, AGVs improve productivity, lower operational costs, and future-proof warehouse operations.
Investing in AGVs is no longer optional—it’s a strategic decision for companies aiming to stay competitive in the rapidly evolving logistics landscape.








